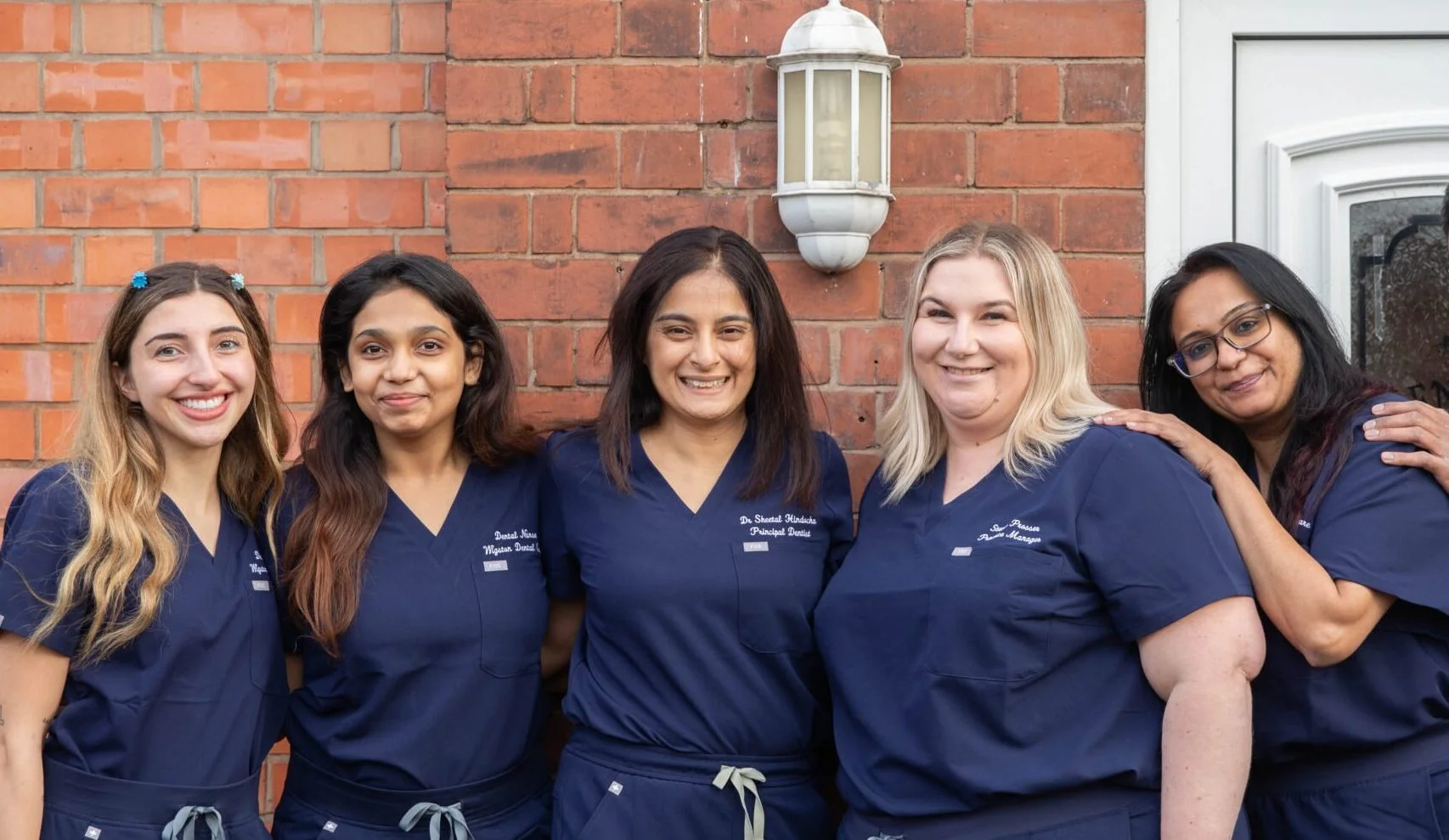
Cardio and strength training are two common workout approaches that are frequently thought of when discussing muscle gain. Although they have different uses in a training regimen, both offer unique advantages. The main distinctions between strength and aerobic exercise, their effects on muscle growth, and which is ideal for muscle building will all be covered in this complete article.
Understanding Cardio vs. Strength Training
Exercises that raise your heart rate and enhance the effectiveness of your cardiovascular system are referred to as cardio or cardiovascular exercise. Walking, swimming, cycling, and running are a few examples. The main benefits of cardio exercises are increased endurance and calorie burning.
Conversely, strength training, sometimes referred to as resistance training, consists of workouts that use weights, resistance bands, or body weights to help build muscle. The goals of these exercises are to build muscle mass, strength, and general power.
How Does Cardio Affect Muscle Building?
Cardio doesn’t directly promote muscle building, but it’s great for heart health, endurance, and fat reduction. Long-term aerobic exercises, particularly those at high intensities, can have a catabolic effect on your muscles, which means that if they are not balanced with strength training and a healthy diet, they can gradually break down muscle tissue.
However, moderate cardio can be beneficial for muscle building in the following ways:
- Improved Blood Flow: Cardio improves circulation, which aids in supplying muscles with nutrition and oxygen, thereby accelerating muscle recovery.
- Fat Loss: Cardio can significantly improve muscular tone and give muscles a more defined appearance by lowering body fat.
- Endurance for Strength Training: Cardio increases general endurance, which enables you to complete more sets and repetitions during strength training.
How Does Strength Training Build Muscle?
Muscle training is the most efficient way to build muscle. The muscle fibers tear minute tears when you lift weights or perform resistance exercises. As these fibers repair, they grow back stronger and larger, leading to muscle growth.
Key benefits of strength training for muscle building include:
- Muscle Hypertrophy: Muscle hypertrophy (muscle growth) is triggered by progressive overload, which involves progressively increasing weight or resistance.
- Increased Metabolism: Gaining muscle raises your resting metabolic rate, which helps you lose weight by burning more calories when you’re at rest.
- Strength Gains: Strength training increases muscle strength in addition to size, which enhances performance in other physical activities.
Cardio vs. Strength Training for Building Muscle: Which One Wins?
Strength training directly targets various muscle groups, including some of the most powerful ones, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes. Notably, the largest muscle in the body, the gluteus maximus, plays a critical role in lower body strength. Exercises like squats, deadlifts, and lunges are excellent for engaging this muscle, promoting both strength and hypertrophy.
- Muscle Growth: Strength exercise encourages growth by directly targeting muscle fibers. Conversely, cardio does not have the same effect on muscle building.
- Hormonal Impact: Human growth hormone (HGH) and testosterone, two growth hormones necessary for muscle growth, are produced in greater quantities during strength exercise. These hormones can be lowered by cardio, particularly vigorous or prolonged cardio, which may prevent muscle growth.
- Caloric Burn vs. Muscle Preservation: Even though cardio burns a lot of calories if done excessively without the right diet, it might cause muscle loss. On the other hand, strength exercise burns calories while preserving and growing muscle.
A Balanced Approach: Combining Cardio and Strength Training
While strength training is essential for muscle building, incorporating cardio into your routine can offer several advantages:
- Heart Health: Cardio strengthens the heart, which is essential for general fitness.
- Fat Loss: Cardio helps burn fat, revealing the muscle mass you’ve worked hard to build.
- Active Recovery: By improving blood flow to the muscles and lowering soreness, light to moderate aerobic exercise can help with muscle rehabilitation.
Tips for Maximizing Muscle Growth
Here are some tips for maximizing muscle growth:
- Prioritize Strength Training: Focus on strength training activities at least three to four times a week if you want to gain muscle.
- Incorporate Cardio Wisely: Incorporate aerobic workouts two to three times per week, but refrain from conducting vigorous aerobics immediately before or after strength training as this could impede muscle building.
- Fuel Your Body Properly: To build and repair muscle tissue, make sure you’re getting enough protein in your diet. It is crucial to eat a balanced diet that contains enough calories and macronutrients.
- Get Enough Rest: Muscle growth occurs during rest, not during exercise. Prioritize sleep and recovery to allow your muscles to grow.
- Healthy Fats: Fats are vital for hormone production, including testosterone and growth hormone. Include sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in your diet.
Conclusion
Strength training is the most effective way to gain muscle because it causes progressive overload, muscle injury, and metabolic stress, all of which directly promote muscle growth. Cardio improves heart health, endurance, and helps people lose weight, but it doesn’t have the same effect on muscle building. Nonetheless, adding moderate exercise to your regimen can hasten muscle recovery, help with fat loss, and enhance cardiovascular health.
Strength training should be prioritized for best results, while cardio should be added for fat loss, endurance, and general health maintenance. To optimize muscular growth, make sure your body is properly nourished and that you allow your muscles adequate time to recover.